The Ultimate Guide to Fuel Dispenser Types: Applications, Features, and Selection for Modern Businesses
07 Jan,2026
The Ultimate Guide to Fuel Dispenser Types: Applications, Features, and Selection for Modern Businesses
Fuel dispensers—also known as gas pumps, petrol pumps, or petrol bowsers in different regions—are the backbone of any refueling operation. Whether you're running a high-volume gas station, managing a fleet depot, or setting up mobile refueling for construction sites, selecting the right fuel dispenser type can directly impact efficiency, safety, compliance, and profitability. This comprehensive guide breaks down the main types of fuel dispensers, their core applications, key technical specifications, and practical tips for choosing the best one for your needs. By understanding these categories, businesses in the oil, gas, LNG, CNG, and EV-adjacent industries can optimize their equipment investments and target high-intent searches like "commercial fuel dispenser", "mini fuel dispenser", and "LNG dispenser".
In today's competitive refueling market, operators face diverse demands: from standard gasoline and diesel delivery to alternative fuels like compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG). Modern fuel dispensing equipment must handle varying flow rates, integrate smart features like RFID and IoT, and meet strict explosion-proof standards. We'll explore hydraulic systems (suction vs. pressure), metering accuracy, nozzle designs, and emerging innovations to give you a complete roadmap.

What Is a Fuel Dispenser? Core Definitions and Regional Variations
At its essence, a fuel dispenser is a precision-engineered system that draws liquid or gaseous fuel from storage tanks, measures it accurately via a flow meter (or fuel pump meter), and delivers it through a hose and nozzle to vehicles, aircraft, marine vessels, or portable containers. Key components include the pump, metering section, controller, display, and payment modules, all housed in an explosion-proof cabinet for safety.
Regional terminology matters for global SEO and buyer intent. In the US and Canada, searches spike for gas pump; in the UK, Australia, and India, petrol pump or petrol bowser dominate; while industrial buyers worldwide use fuel dispenser or fuel dispensing system. These variations tie into the general/definition keyword cluster, including high-volume queries like "what is a fuel dispenser" and "fuel dispenser parts".
Fuel types primarily dictate design: petroleum (gasoline, diesel, kerosene), alcohols (ethanol blends), gases (LPG, CNG, LNG), and specialties (biodiesel, hydrogen). Volatility, flammability, and boiling points influence materials, seals, and pressure ratings—critical for avoiding misfueling or leaks.
Commercial and Industrial Fuel Dispensers: High-Volume Powerhouses
Commercial fuel dispensers and industrial fuel dispensers are built for relentless daily use at gas stations, truck stops, hypermarkets, and large fleet depots. These units handle thousands of transactions per day, prioritizing speed, durability, and multi-product capability.

Key Features and Specs
- Flow rates: 5-200 liters per minute (LPM) per nozzle, supporting 1-8 hoses for simultaneous fueling.
- Hydraulic systems: Submersible pumps for underground tanks (immersed in fuel to prevent air ingestion) or suction pumps (positive displacement gear/piston types creating vacuum).
- Metering: Positive displacement or turbine flow meters with ±0.3% accuracy.
- Nozzles: Pressure-sensitive auto-shutoff, breakaway couplings for safety, and color-coding.
Ideal Applications
- Gas stations: High-traffic retail with pay-at-pump EMV, contactless, and loyalty integration.
- Fleet depots: Card-controlled access for trucks, buses, or logistics companies, reducing theft via RFID.
- Hypermarkets: Self-service islands with vapor recovery for environmental compliance.
Pro Tip: For scalability, choose models with IoT cloud monitoring to track fuel levels, transaction data, and predictive maintenance remotely. Pricing starts at $2,000-$6,800 per unit, influenced by nozzles, payment systems, and certifications.
These dispensers excel in "commercial fuel dispenser" and "gas station fuel dispenser" searches, where buyers seek turnkey solutions from top fuel dispenser manufacturers.
Mini and Mobile Fuel Dispensers: Flexibility for Remote Operations
When full stations aren't feasible, mini fuel dispensers and mobile fuel dispensers provide portable, compact refueling. Often trailer-mounted or skid-based, they're perfect for temporary or off-grid setups.

Ideal Applications
- Construction sites: Diesel delivery to excavators and generators without downtime.
- Farms and agriculture: On-site fueling for tractors and harvesters.
- Mining and remote ops: Rugged units for harsh environments, often ATEX-rated.
- Emergency response: Rapid deployment for disaster relief or military.
Target "mini fuel dispenser", "portable fuel dispenser", and "farm fuel dispenser" for long-tail traffic from niche buyers.
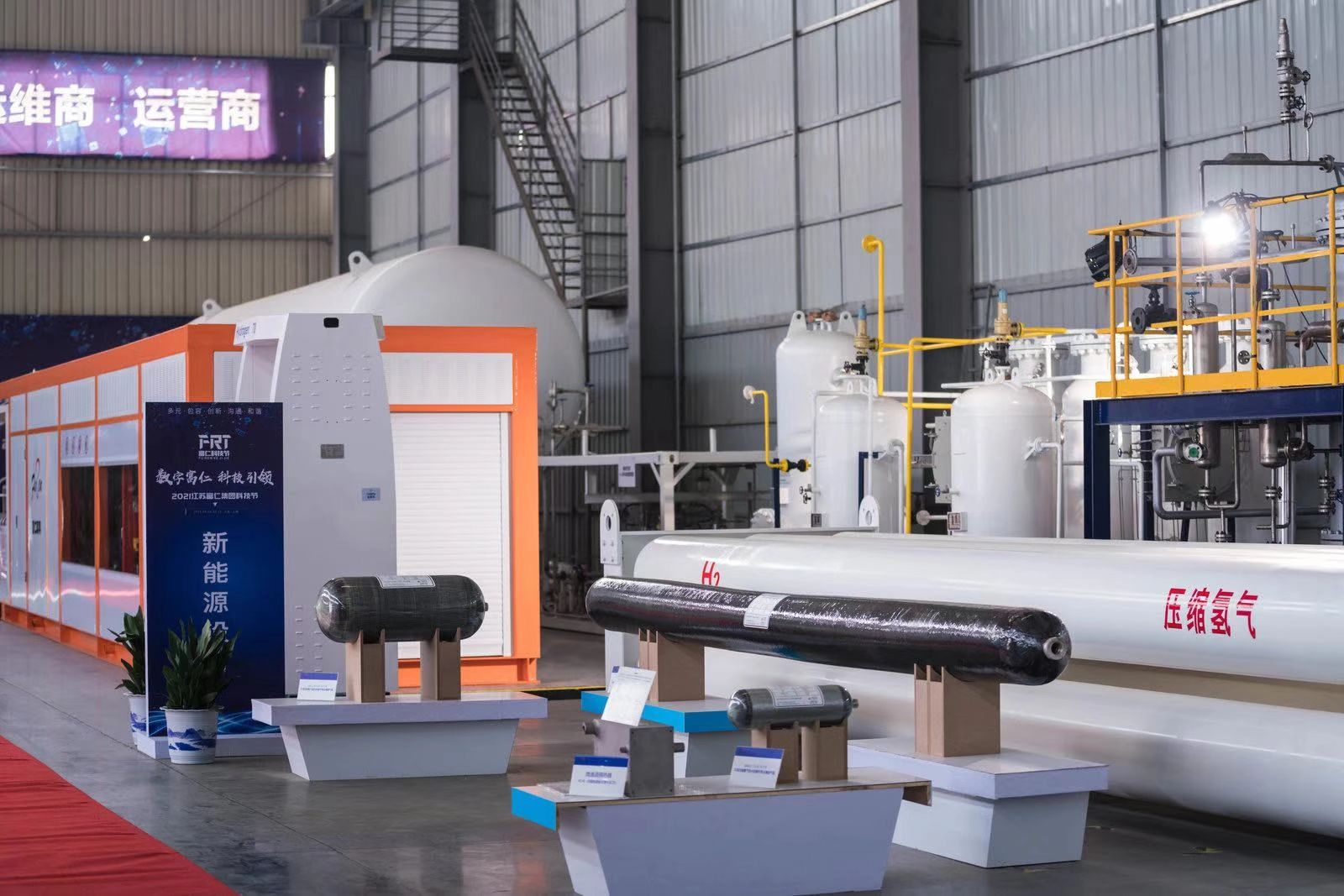
Alternative Fuel Dispensers: LNG, CNG, LPG, and Beyond
As sustainability drives demand, alternative fuel dispensers for LNG, CNG, LPG, and hydrogen are surging. These differ fundamentally from petroleum models due to cryogenic temperatures, high pressures (up to 4,500 PSI), and gaseous states.
LNG and CNG Dispensers
- LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas): Cryogenic pumps vaporize liquid at -162°C, with flow rates of 1-80 kg/min. Features insulated hoses and boil-off gas recovery.
- CNG (Compressed Natural Gas): Compressor-driven, single/double-hoSE setups for fast-fill (5-15 mins) or time-fill overnight.
- Apps: Public CNG stations, fleet conversions (buses, trucks), and LNG marine bunkering.
LPG Dispensers
- Vaporizers convert liquid propane to gas, with 20-100 LPM rates and electronic preset controls.
Emerging: Hydrogen and Biodiesel
- Hydrogen: Ultra-high-pressure dispensers for FCEVs.
- Biodiesel: Corrosion-resistant seals for high-viscosity blends.
"LNG dispenser", "CNG dispenser", and "LPG fuel dispenser" are high-value clusters for green energy projects.
Smart and Automated Fuel Dispensers: The Future of Efficiency
Smart fuel dispensers integrate electronics for RFID fuel dispenser, IoT fuel dispenser, and cashless operations, elevating basic hardware to intelligent systems.
Core Innovations
- RFID/Card Control: Fleet authorization, preventing unauthorized fills.
- Pay-at-Pump: EMV, NFC, QR for seamless transactions.
- IoT/Cloud: Real-time data on volume, leaks, and uptime via apps.
- Automated Features: Pre-set volumes, auto-shutoff, and remote stop.
Apps: Unattended stations, 24/7 fleets. "Automated fuel dispenser" and "cashless fuel dispenser" drive tech-savvy searches.
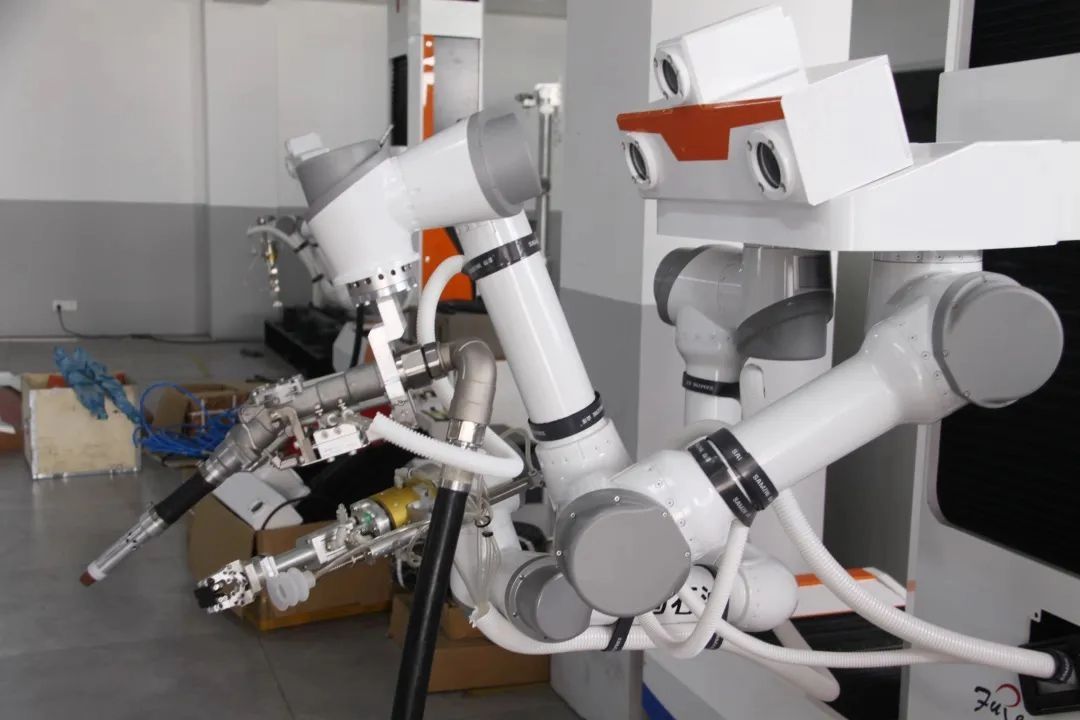
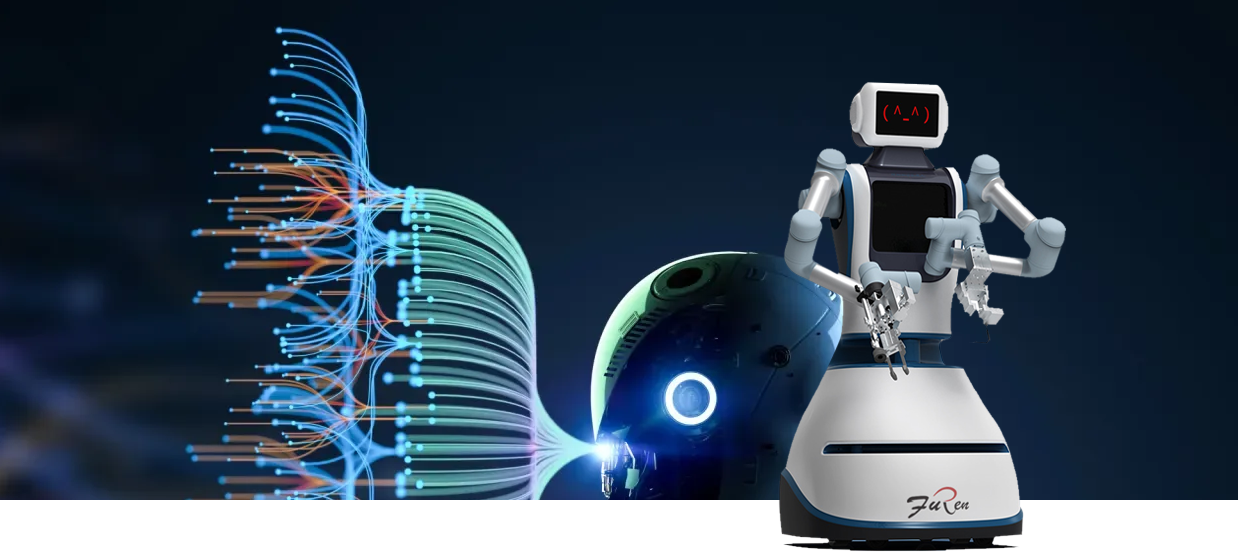
AI Refueling Robots: The Next Frontier
AI refueling robots use double-armed robotics, computer vision, and your patented tech (ZL202011159843.8) for fully autonomous fueling. Benefits: labor savings, 24/7 ops, zero spills. Ideal for high-volume unmanned stations.


How to Choose the Right Fuel Dispenser: Buyer's Checklist
- Assess Needs: Volume, fuel type, location.
- Check Specs: Flow rate, accuracy, power.
- Evaluate Supplier: Certifications, warranties from fuel dispenser suppliers.
- Budget: Factor maintenance .
- Future-Proof: Add IoT/AI.
Maintenance and Compliance for Longevity
Calibrate quarterly (±0.3% accuracy), inspect nozzles/hoses monthly. Lifespan: 15-20 years.
Conclusion: Fuel Your Business Growth
Mastering fuel dispenser types positions your operation for success. From commercial giants to AI robots, the right choice drives revenue. Contact Jiangyin Furen High-Tech for tailored solutions—we've equipped 300+ clients across 20 countries.
TAG:
Previous
Previous:
Related Posts
 Language
Language